How Does Red Light Therapy Work?
How Red Light Masks Can Help Ease Your Shingles Pain
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, afflicts many with its tell-tale painful rash, tingling, and blisters—an unwelcome encore for the chickenpox virus that lies dormant in countless adults worldwide. Amidst the traditional routes of antivirals and pain management, a new contender has emerged: red light therapy (RLT). This novel approach, harnessing the power of specific light wavelengths, is gaining traction as not only a potential panacea for troublesome skin but also as a beacon of hope for those battling shingles-related discomfort. This article delves into the transformative promise of RLT masks, exploring their scientific backing, practical usage, and the anticipated benefits they hold for enhancing skin health and providing much-needed relief from the pains of shingles.

Red Light Therapy into Your Skincare Routine: Steps and Tips
Integrating red light therapy into your skincare routine can be a game-changer, offering a host of benefits like improved skin tone, reduced fine lines, and enhanced collagen production. In this guide, we'll explore the steps and provide tips on how to seamlessly incorporate red light therapy into your daily skincare regimen.

Speed Up Healing & Reduce Scars
Healing from wounds and getting rid of scars can be slow and tough. But what if there was something that could speed up the process? This is where red light therapy masks come in. They use a special kind of light to help your skin heal faster and look better. In this article, we’ll explore how these masks are changing the game in healing cuts and reducing scars, making it an exciting option for anyone looking for a helping hand in their recovery.

Red Light therapy Mask for Acne: Benefits and How-To
Acne is a common skin problem that many people deal with, and it can seriously affect someone’s confidence and how they feel about themselves. That’s where red light therapy (RLT) comes in. It’s a treatment that uses light to help improve skin condition, and it has shown promise in treating acne and reducing skin inflammation.
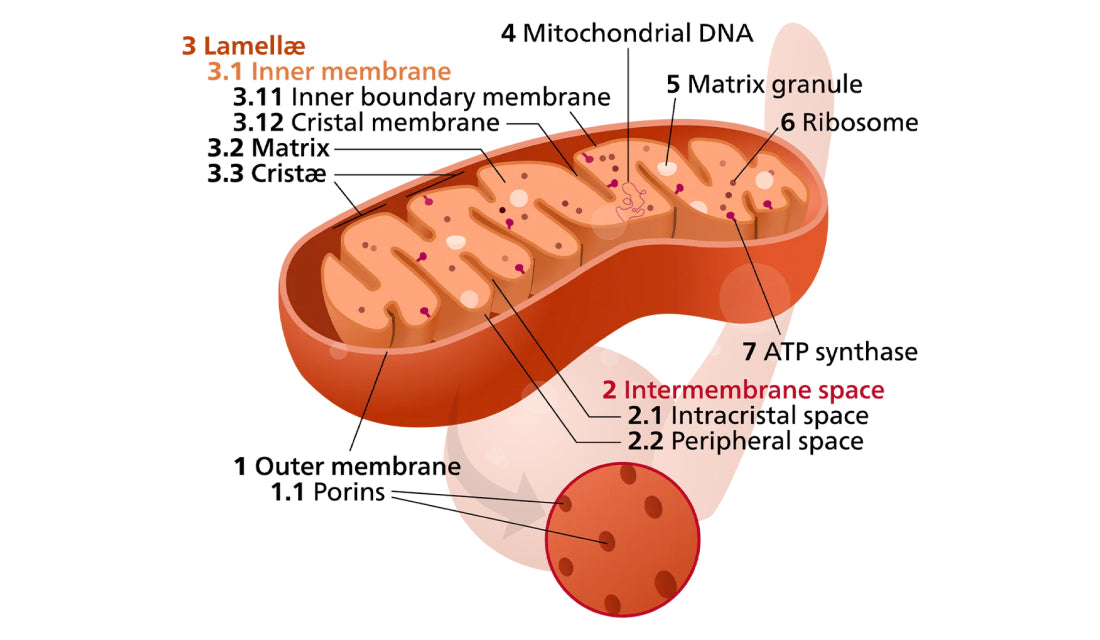
Mitochondrion
Mitochondria are the engines within all biological cells responsible for generating life and energy. Our mitochondria produce cellular energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). Every cell in our body continuously produces and utilizes substantial amounts of ATP to provide fuel.
Image Source
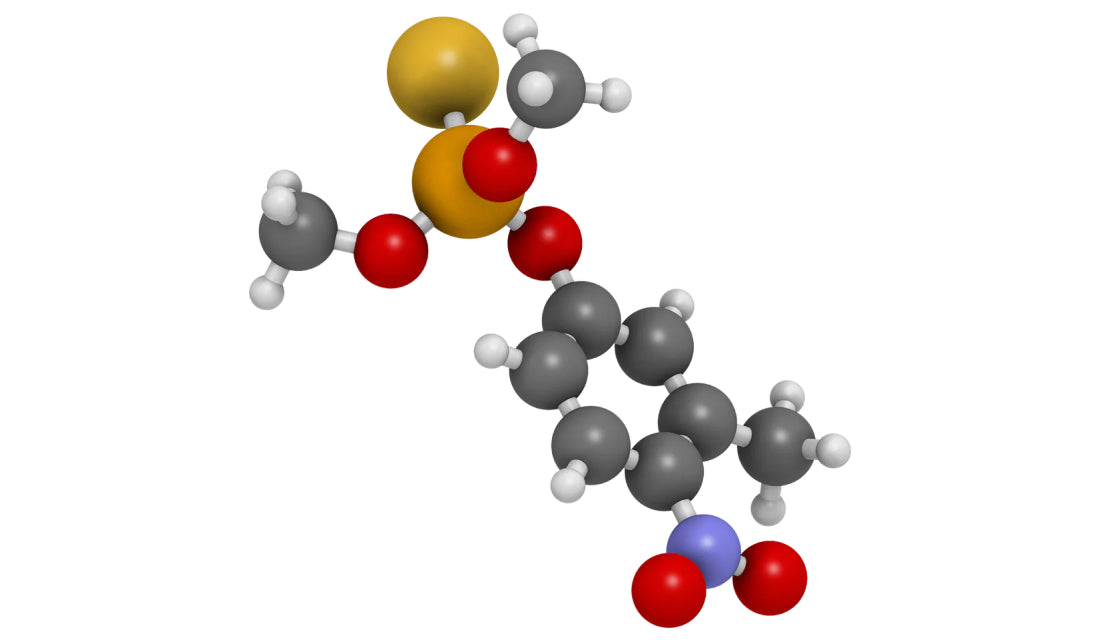
ATP
Mitochondria are the engines that produce life and energy within all living cells, producing cellular energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Every cell in our body is constantly producing and using large amounts of ATP to provide fuel.
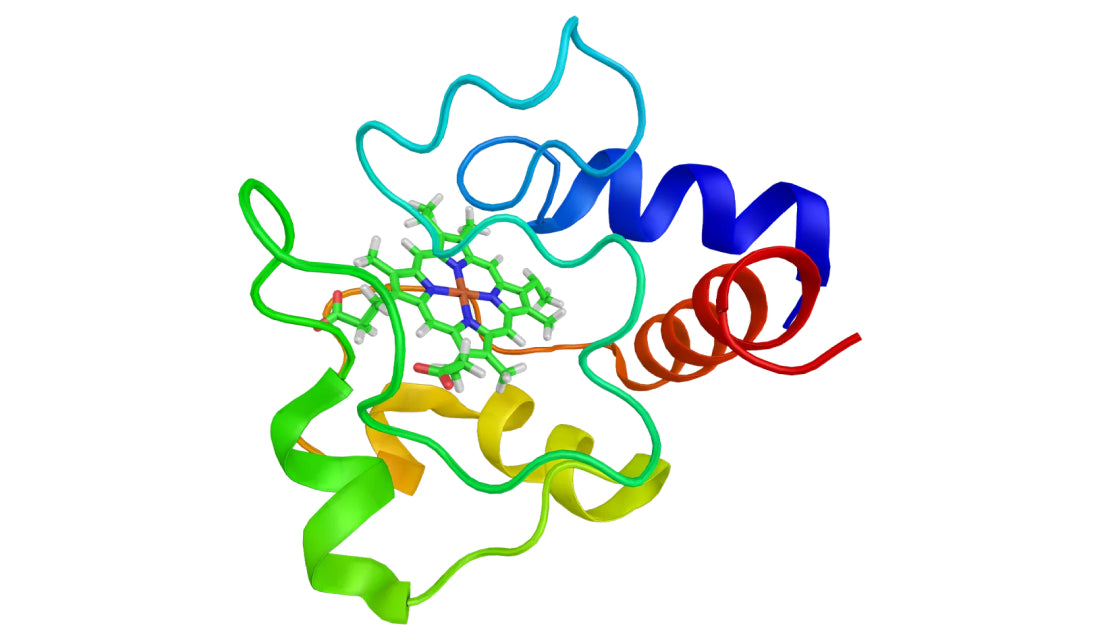
Cytochrome c
Cytochrome c is a small protein located in the inner mitochondrial membrane,serving as a crucial component of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration.This protein is involved in transferring electrons between complex III and complex IV of the electron transport chain,ultimately contributing to the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate),which is the cell's primary source of energy.Cytochrome c plays a pivotal role in the aerobic respiration process, helping to generate energy from nutrients consumed by the cell.